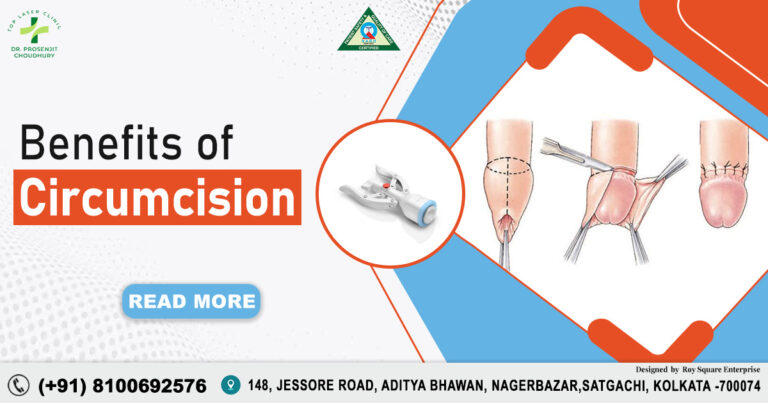
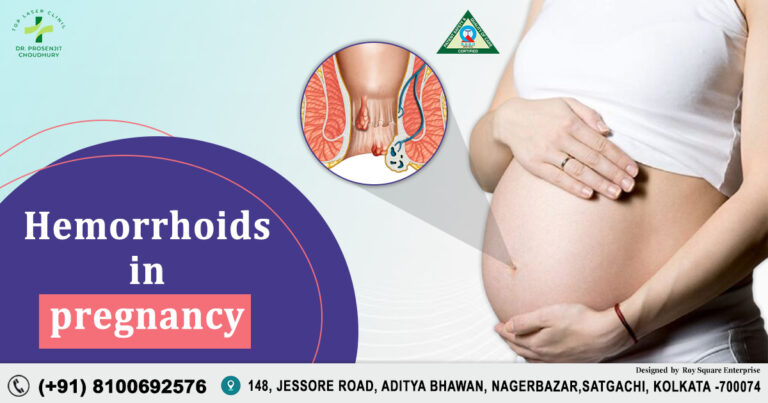
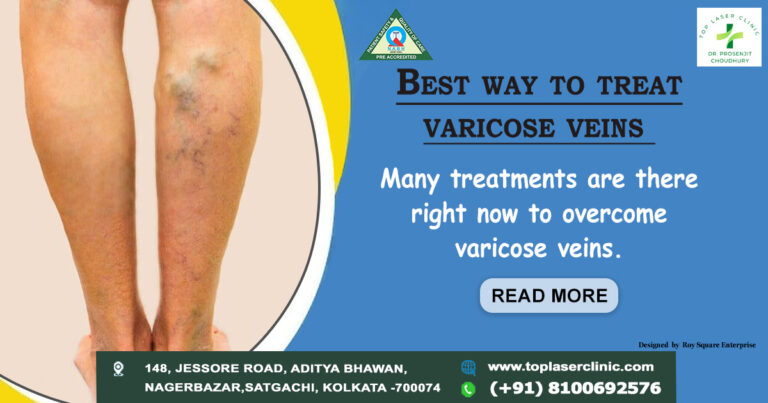
Table of Contents
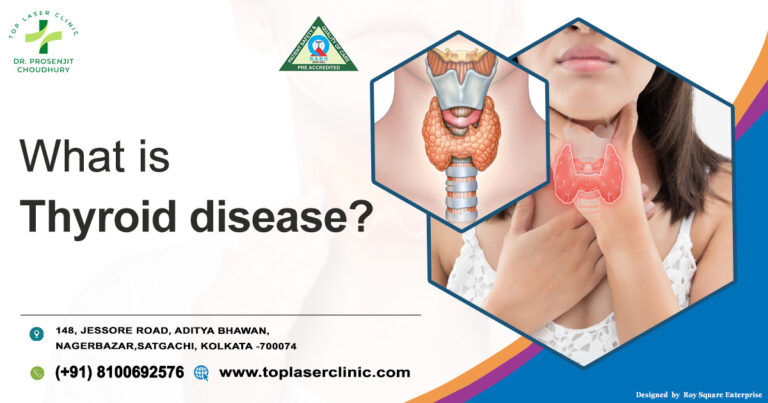
The butterfly-shaped thyroid gland is located below the larynx (Adam’s apple). It circulates hormones to your body to give support all your metabolic processes. But when your thyroid gland produces too much or too little hormones, then it causes thyroid disease. Thyroid Nodules is a condition of thyroid disease, where you see lumps on your gland. The lumps can be solid or fluid-filled. These are generally non-cancerous but sometimes they can be harmful and invite cancer. If they are non-cancerous then you don’t need any treatment. If required, they are treatable also.
Symptoms of Thyroid Nodule
Symptoms related to thyroid nodules are lumps in the neck area which is clearly visible. Other problematic symptoms are swelling, pain in the throat and trouble with swallowing or breathing.
Hyper-functioning thyroid nodules can activate overproduction of thyroid hormone, which we call hyperthyroidism. Symptoms include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Weight loss
- Nervousness
- Increased appetite
- Diarrhea
- Heat intolerance
- Light menstrual bleeding or missed periods
Thyroid nodules are also associated with Hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland produces less hormone levels. Symptoms include:
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Fatigue
- Frequent or heavy menstrual bleeding
Causes of Thyroid Nodules
The actual causes of getting nodules are not fully known, but some conditions may be responsible for it. Those possible conditions are:

- Iodine Deficiency: Lack of iodine deficiency in your diet can lead to thyroid nodule formation.
- Thyroid Adenoma: A thyroid adenoma is an abnormal growth of thyroid tissue. It’s usually benign and may produce excess thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism.
- Autoimmune disease: Hashimoto’s disease, can cause thyroid inflammation and nodule buildup.
- Hormonal level changes: An imbalance of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) level can cause nodules to form.
- Thyroid cancer: Rarely in some cases thyroid nodules build because of thyroid cancer.
- Family history: Family history plays a vital role here. A family history of thyroid nodules or cancer increases the risk of getting affected by it.
Types of Thyroid Nodules
There are several types of thyroid nodules. Some of them are so small that it’s may not noticeable but when they grow bigger, they start giving discomfort. Most of them are benign and being non-cancerous they are easily treatable.
- Thyroid Adenoma: Thyroid adenomas are benign growths of normal thyroid tissue that come in various forms. They typically don’t require treatment unless they cause compressive symptoms.
- Multinodular Goiter: If several nodules are found in the thyroid, then it’s called a multinodular goiter. Multinodular goiter causes the thyroid to produce too much thyroxine, which may result in hyperthyroidism. These are called toxic multinodular goiter.
- Thyroid cysts: Thyroid cysts are fluid-filled nodules in the thyroid. Some cysts are congenital (Present from birth). They are usually benign. Some thyroid cysts may require watchful waiting to ensure that they don’t turn into cancer.
- Thyroid cancer: Thyroid cancer forms when a cancer cell develops in the thyroid nodule. The multiple types of thyroid cancer are – Papillary thyroid cancer, Follicular thyroid cancer, Hurthle thyroid cancer, Medullary thyroid cancer and poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Among them, the most common thyroid cancers are Papillary & Follicular. These are less aggressive than others.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodule
Self-observation comes first. You may feel a lump near your Adam’s apple, when you touch your neck. If you notice this you should seek guidance for this.
Your doctor first asked about your symptoms, medical history and family history. Then they may suggest you to do some tests so that they can find out the type of nodule or it is cancer or not. Those tastes are:
- Blood test: Blood tests are obvious to check the thyroid hormone levels (TSH). Through this, we can understand if the thyroid nodule produces excess hormone (Hyperthyroidism) or less hormone (Hypothyroidism).
- Ultrasound: High-frequency radio waves are used to produce a detailed image of the neck. This non-invasive imaging test helps doctors diagnose and assess thyroid nodules and determine their size, shape, and number. It can also distinguish between cysts and potentially more serious conditions. Additionally, it can guide doctors during a biopsy procedure.
- Thyroid nodule biopsy: If necessary, your doctor may perform a biopsy to determine if the nodule is cancerous. A delicate nodule will be inserted into a nodule to collect a small cell sample. Then it will be observed under a microscope in a lab.
Treatment of Thyroid Nodule
Treatment of thyroid nodules depends on the type of nodule you have. The available thyroid nodule treatment options are:

- Watchful waiting
Small and benign nodules may not need any treatment. So, your doctor can suggest you to wait and observe the nodule with an ultrasound.
- Radioactive Iodine Ablation
The radioactive iodine ablation process is used to treat the hyperactive thyroid nodule. When your thyroid gland absorbs the radioactive iodine it starts to shrink.
- Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is another way to cure your thyroid nodule. It is a minimal invasive procedure that uses heat to shrink the nodule.
- Surgery
Surgical removal of the nodule is used in severe cases. If you notice suspicious or cancerous growth, then surgery to take out the nodules is the best option.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a thyroid nodule?
Answer: A thyroid nodule is an abnormal growth on the thyroid gland, which can be solid or fluid-filled.
- What causes thyroid nodules?
Answer: The exact cause is often unknown, but they can be caused by iodine deficiency, thyroid inflammation, genetics.
- Are thyroid nodules common?
Answer: Yes, thyroid nodules are common, especially in women.
- What are the symptoms of thyroid nodules?
Answer: Many thyroid nodules do not cause symptoms, but some may cause neck swelling, pain, difficulty swallowing, or breathing.
- How are thyroid nodules diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, thyroid tests, ultrasound, and sometimes a biopsy.
- Do all thyroid nodules require treatment?
Answer: No, not all thyroid nodules require treatment. Small, benign nodules may only need monitoring.
- What are the treatment options for thyroid nodules?
Answer: Treatment options include watchful waiting, radioactive iodine ablation, radiofrequency ablation and surgery.