Table of Contents
THYROID
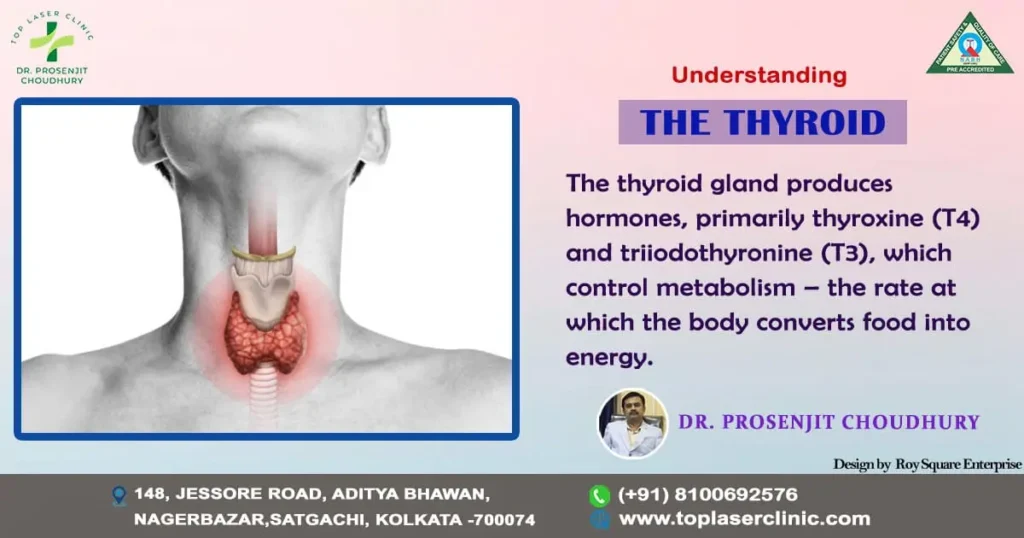
The thyroid is a little gland in the neck that resembles a butterfly and is essential for controlling a number of body processes. Despite its modest size, the thyroid wields significant influence over metabolism, energy levels, and overall well-being. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the thyroid gland, exploring its functions, common disorders, and ways to maintain thyroid health.
Understanding the Thyroid:
The thyroid gland produces hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which control metabolism – the rate at which the body converts food into energy. This intricate process involves the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, forming the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), stimulating the pituitary gland to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH, in turn, prompts the thyroid gland to produce and release T4 and T3, maintaining a delicate balance.
Common Thyroid Disorders:
1. Hypothyroidism:
- Happens when the thyroid doesn’t make enough hormones.
- Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, depression, and sensitivity to cold.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s disease) is a common cause.
2. Hyperthyroidism:
- Characterized by an overactive thyroid, leading to excessive hormone production.
- Anxiety, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, and weight loss are possible symptoms.
-One frequent autoimmune cause is Graves’ disease.
3. Goiter:
- An enlarged thyroid gland often resulting from iodine deficiency.
- May cause swelling in the neck and difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Maintaining Thyroid Health:
Maintaining thyroid health involves a holistic approach that encompasses a well-balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and awareness of potential risk factors.
Balanced Diet:
Ensure a diet rich in essential nutrients, including iodine, selenium, zinc, and vitamin D.
Incorporate sources of iodine such as seafood, dairy, and seaweed.
Include selenium-rich foods like Brazil nuts, fish, and whole grains.
Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains for overall nutritional balance.

i. Regular Exercise:Engage in regular physical activity to support metabolism and maintain a healthy weight.A combination of aerobic exercises (e.g., walking, jogging) and strength training can be beneficial.
ii. Stress Management:Chronic stress can impact thyroid function. Practice stress-relieving methods like yoga, deep breathing, mindfulness, or meditation.Ensure adequate sleep, as sleep is crucial for overall hormonal balance.
iii. Limit Iodine Intake:While iodine is essential for thyroid function, excessive intake can be detrimental. Avoid excessive iodine supplementation unless advised by a healthcare professional.
iv. Regular Check-ups:Schedule regular thyroid function tests, especially if you have a family history of thyroid disorders or experience symptoms.Routine check-ups allow for early detection and intervention if any thyroid abnormalities are identified.
v. Limit Processed Foods:Processed foods, particularly those high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats, can contribute to inflammation and may impact thyroid function.Opt for a diet that emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods.
vi. Avoid Smoking:Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of thyroid disorders. Quitting smoking is beneficial for overall health, including thyroid health.
vii. Moderate Alcohol Consumption:Excessive alcohol intake may interfere with thyroid function. If you drink alcohol at all, do it in moderation.
viii. Stay Hydrated:Proper hydration is essential for overall health, including thyroid function. Aim for an adequate intake of water throughout the day.
ix. Understand Medications:Some medications can affect thyroid function. If you are on medication, discuss potential impacts on the thyroid with your healthcare provider.
x. Sunlight Exposure:Adequate exposure to sunlight helps in the natural synthesis of vitamin D, which is important for thyroid health. Spend time outdoors, but always practice sun safety.
While the thyroid gland typically resides in the neck, variations in its embryonic development can lead to anomalies such as lateral aberrant thyroid. This rare condition involves the presence of thyroid tissue in locations other than the usual midline position. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the peculiarities of lateral aberrant thyroid, exploring its causes, clinical manifestations, and potential management strategies.
Understanding Lateral Aberrant Thyroid:
The development of the thyroid gland originates from the primitive pharynx, with the thyroid tissue migrating from its initial position to the midline of the neck. Lateral aberrant thyroid occurs when some thyroid tissue deviates from this path and ends up in locations not commonly associated with the thyroid gland. These anomalous thyroid tissues can be found along the course of the thyroglossal duct or in lateral locations such as the base of the tongue, the mediastinum, or even within the lateral neck.
Causes and Diagnosis:
The exact cause of lateral aberrant thyroid remains elusive, with genetic and environmental factors potentially playing a role in its development. Diagnosis often involves imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, or scintigraphy, which help identify the presence and location of the aberrant thyroid tissue. Symptoms, if present, may vary depending on the size and functionality of the ectopic tissue.
Clinical Manifestations:
Lateral aberrant thyroid is typically asymptomatic, and the condition may only be discovered incidentally during diagnostic imaging for unrelated issues. However, if the ectopic thyroid tissue is functional, symptoms resembling those of typical thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, may manifest.
Management and Treatment:
Management of lateral aberrant thyroid depends on factors such as the size, location, and functionality of the ectopic tissue. Asymptomatic cases may not require intervention, while functional anomalies may necessitate treatment with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Surgical removal may be considered in cases where the ectopic tissue causes symptoms, compresses nearby structures, or poses a risk of malignancy.
Lateral aberrant thyroid is a rare anomaly that highlights the intricate nature of embryonic development. While it often presents without noticeable symptoms, its presence can be identified through advanced imaging techniques. Understanding the causes, clinical manifestations, and potential management strategies for lateral aberrant thyroid contributes to a comprehensive appreciation of thyroid disorders, showcasing the fascinating complexity of the human body’s developmental processes. If you suspect any thyroid-related issues or anomalies, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Thyroxine:
Thyroxine, a vital hormone produced by the thyroid gland, plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism and maintaining overall physiological balance. However, when the thyroid gland goes into overdrive, hypersecretion of thyroxine, also known as hyperthyroidism, can occur. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments associated with this condition, shedding light on the impact of an excessively active thyroid.
Causes of Hypersecretion of Thyroxine:
Hyperthyroidism is often caused by an overstimulated thyroid gland, resulting in the excessive production and release of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The most common causes include:
• Graves’ Disease:
-An autoimmune condition when the body’s immune system erroneously targets the thyroid gland.
-Antibodies stimulate the thyroid, leading to increased hormone production.
• Toxic Nodular Goiter:
-Formation of nodules (lumps) in the thyroid gland, which become overactive and produce excess hormones.
• Thyroiditis:
-Inflammation of the thyroid gland, causing the release of stored thyroid hormones into the bloodstream.
• Excessive Iodine Intake:
-High levels of iodine, whether from diet or medication, can trigger hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism:
The symptoms of hypersecretion of thyroxine can vary in severity and may include:
• Weight Loss:
-Despite increased appetite, individuals may experience unexplained weight loss.
• Increased Heart Rate:
-Elevated heart rate (tachycardia) and palpitations.
• Nervousness and Anxiety:
-Restlessness, irritability, and heightened anxiety levels.
• Heat Intolerance:
-Difficulty tolerating heat, excessive sweating, and warm, moist skin.
• Fatigue and Weakness:
-Paradoxically, individuals may feel tired despite the increased metabolic rate.
• Tremors:
-Fine tremors in the hands or fingers.
Treatment Options:
The management of hyperthyroidism aims to normalize thyroid hormone levels and alleviate symptoms. Common treatment approaches include:
Antithyroid Medications:
Drugs like methimazole or propylthiouracil reduce the production of thyroid hormones.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
Radioactive iodine is taken orally, and it selectively destroys thyroid tissue.
Beta-Blockers:
Medications to control symptoms like rapid heartbeat and tremors.
Thyroidectomy:
Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be recommended in certain cases.
In conclusion of hyperthyroidism, it can be said that hypersecretion of thyroxine can significantly impact an individual’s well-being, affecting various bodily functions. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial to address symptoms and prevent potential complications. If you suspect symptoms of hyperthyroidism, seeking medical attention for thorough evaluation and personalized treatment is essential for restoring thyroid function and promoting overall health.

Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer, though often treatable, can pose significant challenges when it reaches an advanced stage. In this blog post, we’ll explore the characteristics of advanced thyroid cancer, its potential causes, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and the ongoing advancements in medical research that offer hope for individuals facing this complex condition.
Understanding Advanced Thyroid Cancer:
Thyroid cancer typically begins as abnormal cell growth within the thyroid gland. When the disease progresses to an advanced stage, it may extend beyond the thyroid, invade nearby structures, or metastasize to distant organs. Common types of advanced thyroid cancer include anaplastic thyroid cancer, poorly differentiated thyroid cancer, and advanced forms of differentiated thyroid cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact causes of thyroid cancer are not always clear, but certain risk factors may contribute to its development. These include:
Radiation Exposure:
Previous exposure to high doses of radiation, especially during childhood, is a known risk factor.
Genetic Factors:
Inherited genetic mutations, such as those in the RET or BRAF genes, may increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
Gender and Age:
Thyroid cancer is more common in women, and the risk increases with age.
Family History:
A family history of thyroid cancer may elevate the risk for some individualsDiagnostic Approaches:
Advanced thyroid cancer is often diagnosed through a combination of imaging studies, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI, and biopsy to analyze tissue samples. Blood tests may also be conducted to assess thyroid function and detect specific markers associated with thyroid cancer.
Treatment Options:
The treatment of advanced thyroid cancer is multidisciplinary, involving a combination of surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, targeted therapy, and, in some cases, external beam radiation. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the type of thyroid cancer, the extent of the disease, and the individual’s overall health.
Ongoing Research and Hope for the Future:
Medical research continues to explore novel approaches for the treatment of advanced thyroid cancer. Immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and precision medicine are among the innovative strategies being investigated to improve outcomes and reduce the side effects associated with traditional treatments.
Advanced thyroid cancer presents a formidable challenge, requiring a comprehensive and personalized approach to treatment. While the journey may be complex, advancements in research and a deeper understanding of the disease offer hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals facing advanced stages of thyroid cancer. Seeking timely medical attention, staying informed about treatment options, and participating in ongoing research can contribute to a more optimistic outlook for those navigating this intricate terrain.
The thyroid gland may be small, but its impact on overall health is immense. Understanding its functions, recognizing common disorders, and adopting a proactive approach to thyroid health can contribute to a balanced and energized life. By incorporating healthy lifestyle habits and seeking medical guidance when needed, individuals can empower themselves to support their thyroid and maintain optimal well-being.