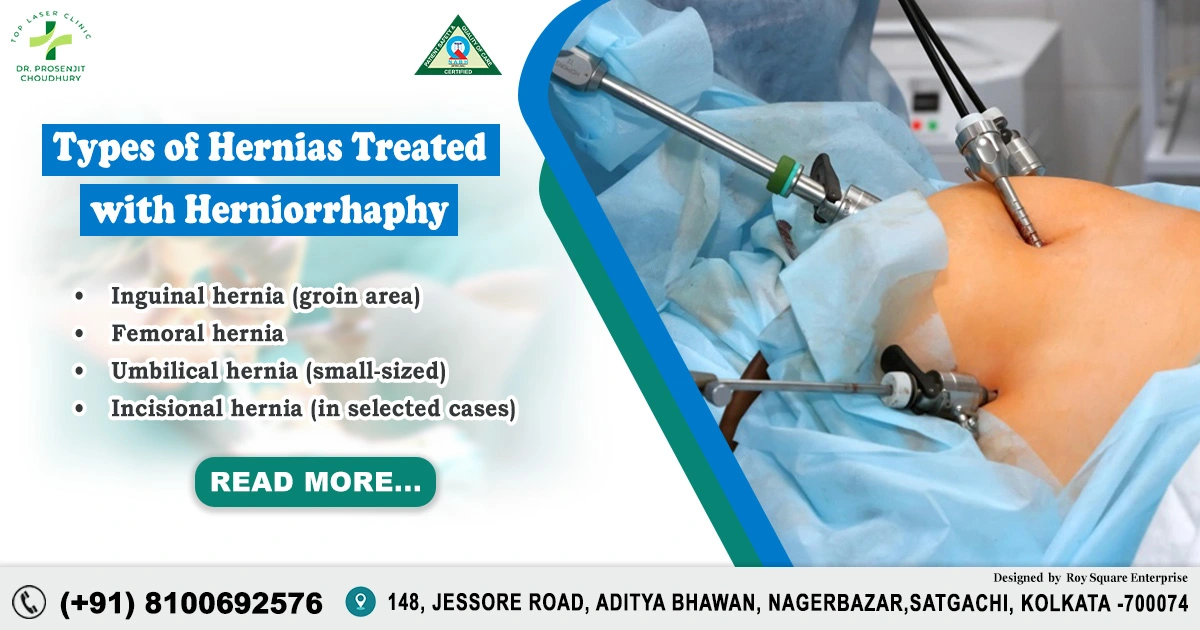
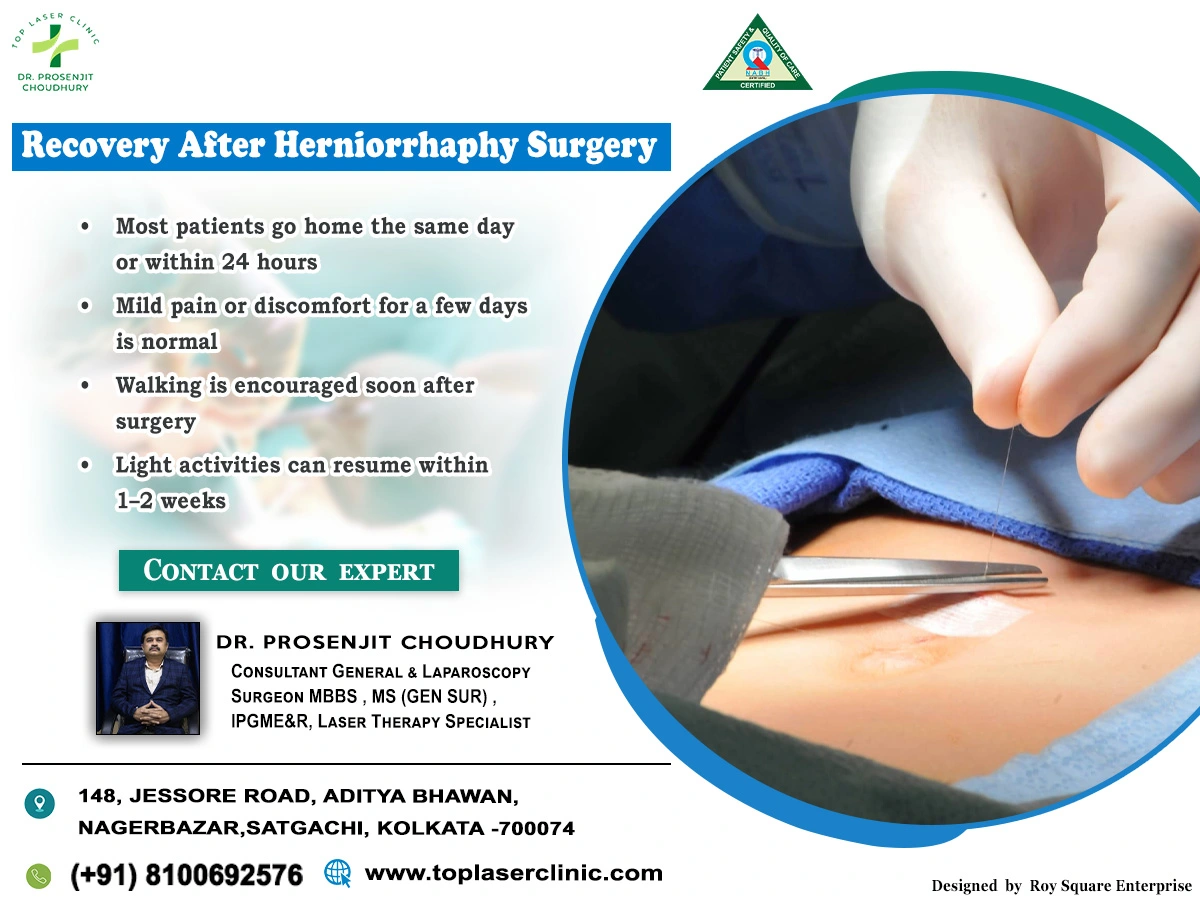
Table of Contents
Physiotherapy for Varicose Veins

Varicose veins are a common but often misunderstood vascular condition that affects a significant number of people worldwide. These swollen, twisted veins can cause discomfort and aesthetic concerns, impacting the quality of life for those affected. In this blog post, we will explore the role of physiotherapy in promoting vascular health, strengthening leg muscles, and enhancing overall well-being. However, prior to that we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for managing varicose veins in short.
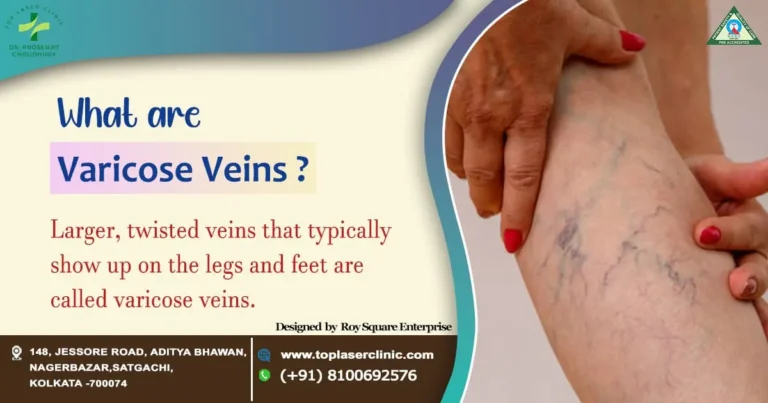
What are Varicose Veins?
Larger, twisted veins that typically show up on the legs and feet are called varicose veins. They develop when the valves in the veins fail to function properly, causing blood to pool and exert increased pressure on the vein walls. This can result in the characteristic bulging and twisting of the veins that many people associate with varicose veins.
Causes of Varicose Veins:
Varicose veins can develop due to a number of circumstances, such as:
- Genetics: Varicose veins are more common in families where the problem runs in the family.
- Age: As people age, the elasticity of vein walls decreases, making them more prone to dilation and the development of varicose veins.
- Gender: Women are more prone to develop varicose veins than men, partly due to hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Jobs that involve long periods of standing or sitting can impede blood flow, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins, contributing to the development of varicose veins.
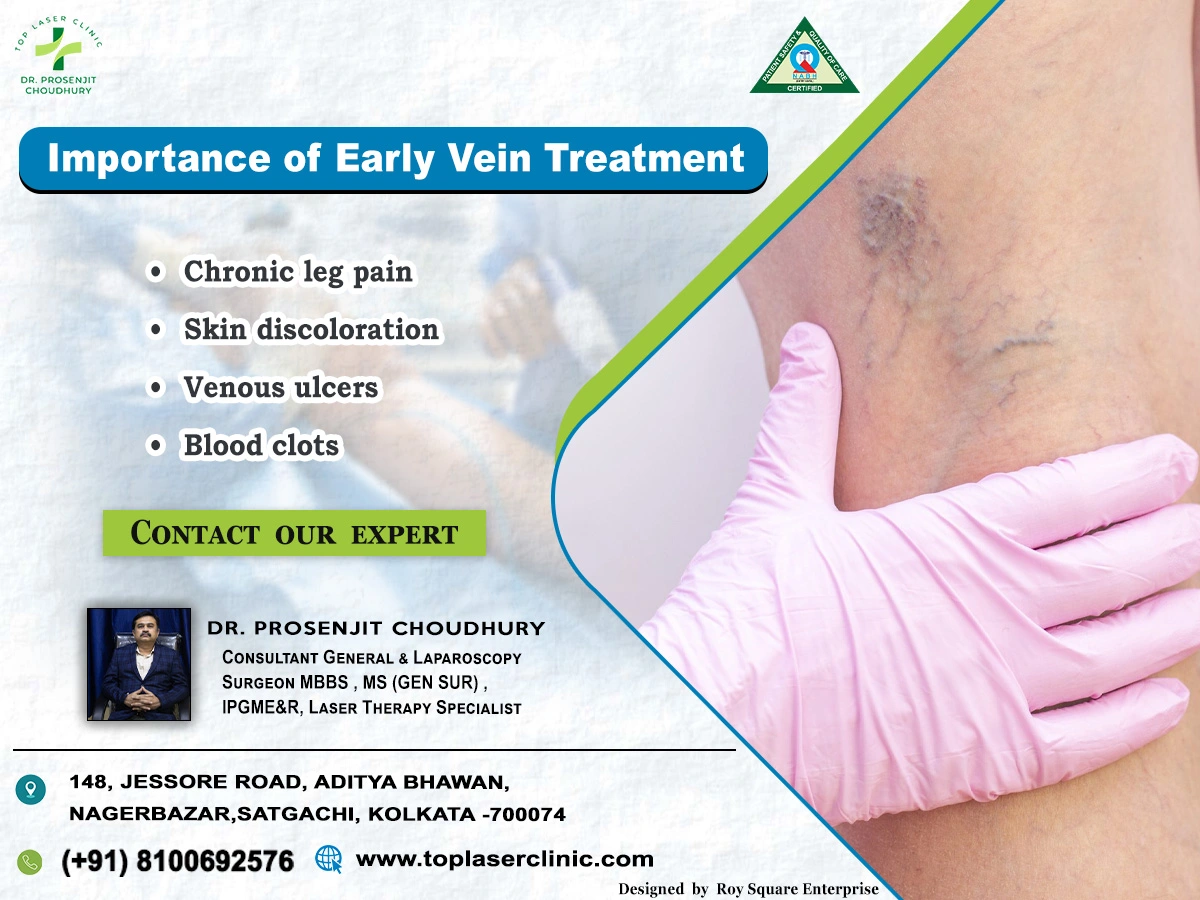
Symptoms of Varicose Veins:
Varicose veins may be asymptomatic for some individuals, while others may experience various symptoms, including:
- Pain or Aching: Discomfort or aching in the affected area, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
- Swelling: Swelling in the legs and ankles due to fluid build-up.
- Itching and Burning: Skin irritation, itching, or a burning sensation around the affected veins.
- Skin Changes: Changes in skin colour or the development of sores near the affected veins.

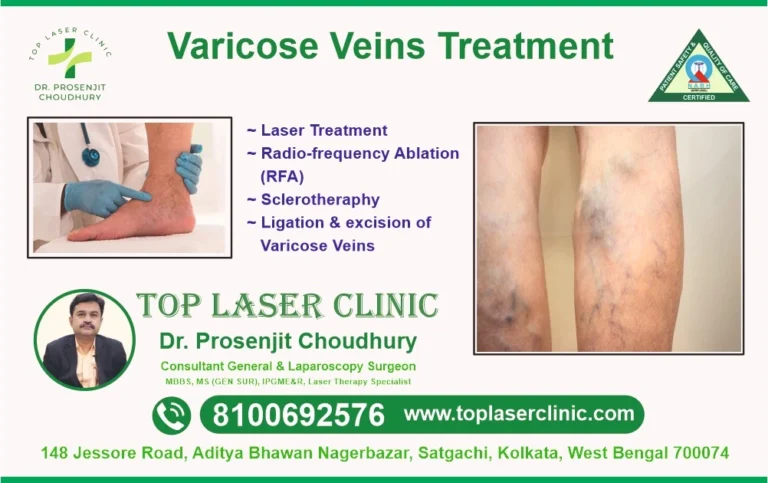
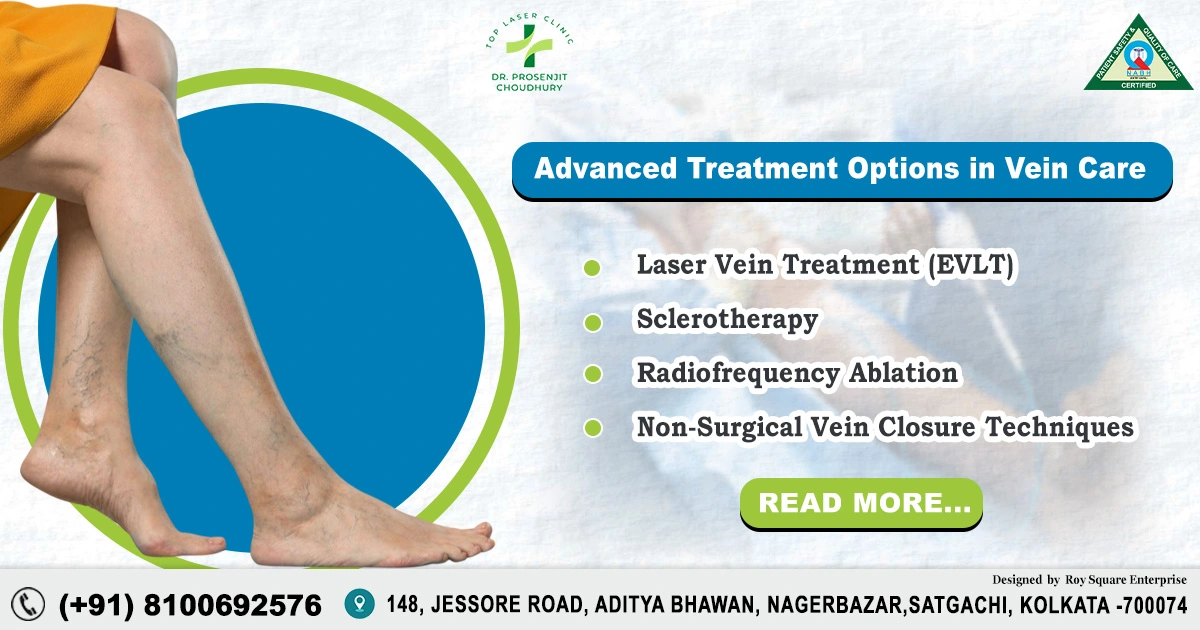
Treatment Options:
Several treatment options are available for managing varicose veins, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical interventions:
- Lifestyle Modifications:Regular exercise to improve circulation.Weight management to reduce pressure on veins.Try to avoid prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
- Compression Stockings:Wearing compression stockings to promote blood flow and reduce swelling.
- Sclerotherapy:Injection of a solution into the affected veins to cause them to collapse and fade.
- Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT):A minimally invasive procedure using laser energy to seal the affected veins.
- Surgical Options:Vein stripping or ligation in severe cases.
While various treatment options are available, physiotherapy stands out as a valuable and non-invasive approach to managing and alleviating the symptoms associated with varicose veins.
Understanding Physiotherapy for varicose veins
Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, involves the use of physical methods, exercises, and manual techniques to restore, maintain, and improve physical function. In the context of varicose veins, physiotherapy focuses on enhancing blood circulation, reducing swelling, and strengthening the muscles that support the venous system.
Benefits of Physiotherapy for Varicose Veins:
- Improved Circulation:
Physiotherapy includes exercises and techniques that promote blood circulation, helping to reduce the pooling of blood in the affected veins. Improved circulation contributes to overall vascular health and minimizes the risk of complications.
- Muscle Strengthening:
Physiotherapists design exercise programs to target specific muscle groups, particularly those in the legs. Strengthening these muscles helps support the venous system, reducing the pressure on veins and aiding in blood flow back to the heart.
- Compression Therapy:
Physiotherapists may recommend compression stockings or bandages to help reduce swelling and improve blood circulation in the legs. Properly fitted compression garments can be a valuable component of a comprehensive physiotherapy plan.
- Range of Motion Exercises:
Physiotherapy includes movements that promote flexibility and joint mobility. These exercises can be beneficial for individuals with varicose veins, preventing stiffness and discomfort associated with prolonged periods of inactivity.
- Education and Lifestyle Modification:
Physiotherapists educate patients about lifestyle changes that can positively impact their vascular health. This may include advice on maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and adopting ergonomic practices to reduce the risk of exacerbating varicose veins.
- Manual Therapy Techniques:
Manual therapies such as massage and manual lymphatic drainage may be employed by physiotherapists to reduce swelling, alleviate pain, and enhance the overall well-being of individuals with varicose veins.
- Posture Correction:
Correcting posture is crucial in managing varicose veins. Physiotherapists can assess and provide guidance on maintaining proper posture during various activities, reducing unnecessary strain on the venous system.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Professionals:
Physiotherapy for varicose veins is often part of a collaborative approach involving various healthcare professionals, including vascular specialists. Physiotherapists work closely with patients to tailor treatment plans based on individual needs and the severity of the condition.
Physiotherapy emerges as a valuable and holistic approach in the management of varicose veins. By focusing on improving circulation, strengthening leg muscles, and promoting overall well-being, physiotherapy empowers individuals to take an active role in their vascular health. If you are dealing with varicose veins, consider consulting with a physiotherapist to develop a personalized plan that addresses your unique needs and enhances your quality of life.
Benefits of Massage for Varicose Veins:
- Improved Blood Circulation:
Massage helps stimulate blood flow, particularly in the affected areas. By applying gentle pressure and specific techniques, massage encourages blood to move through the veins more effectively, reducing the likelihood of blood pooling and congestion.
- Reduced Swelling and Edema:
The gentle manipulation of tissues during a massage helps in draining excess fluid from the legs, reducing swelling (edema). This can provide significant relief to individuals experiencing discomfort and heaviness associated with varicose veins.
- Relief from Pain and Discomfort:
Massage therapy can alleviate pain and discomfort associated with varicose veins by relaxing the muscles, reducing tension, and promoting a sense of well-being. Targeted massage techniques can specifically address areas with increased sensitivity.
- Stimulation of Lymphatic Drainage:
Massage supports the lymphatic system, which plays a crucial role in removing waste and excess fluids from the body. By enhancing lymphatic drainage, massage contributes to the reduction of swelling and promotes a healthier vascular system.
- Improved Muscle Function:
Varicose veins can lead to weakened muscles in the legs. Massage helps in toning and relaxing these muscles, improving their function and providing additional support to the venous system.
- Enhanced Mental Well-being:
Beyond the physical benefits, massage has a positive impact on mental well-being. The relaxation induced by massage can help reduce stress and anxiety, which are factors that can contribute to the exacerbation of varicose veins symptoms.

Considerations Before Getting a Massage-
i. Consultation with a Healthcare Professional:Before undergoing massage therapy for varicose veins, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
ii. Choose a Qualified Massage Therapist:Opt for a licensed and experienced massage therapist who is knowledgeable about varicose veins. They can tailor the massage techniques to address your specific needs and ensure safety.
iii. Gentle Techniques:Inform your massage therapist about your varicose veins, and they can use gentle techniques to avoid putting excessive pressure on the affected areas.
Massage therapy offers a natural and soothing approach to managing the symptoms of varicose veins in the legs. By promoting better circulation, reducing swelling, and providing overall relief, massage can be a valuable addition to a comprehensive treatment plan. Always seek advice from your healthcare provider before starting any new therapeutic regimen, and enjoy the soothing benefits that massage can bring to your journey towards healthier, more comfortable legs.