Gallstones are a very common yet often misunderstood medical condition affecting millions worldwide. They can cause sudden abdominal pain, digestive issues, and sometimes severe complications if left untreated. Understanding gallstones in detail—from their causes and symptoms to diagnosis, treatment, and recovery—can help patients take timely action.
In this blog, we’ll cover everything about gallstones in a simple yet professional way. We will also highlight expert insights from Dr. Prosenjit Choudhury, Consultant General & Laparoscopy Surgeon | MBBS, MS (Gen Surg.), IPGME&R | Best in Laser & Minimally Invasive Surgery, who has treated numerous patients successfully with advanced surgical techniques.
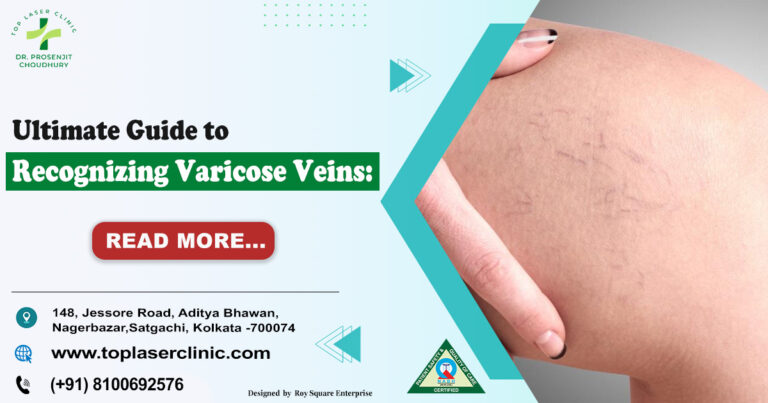
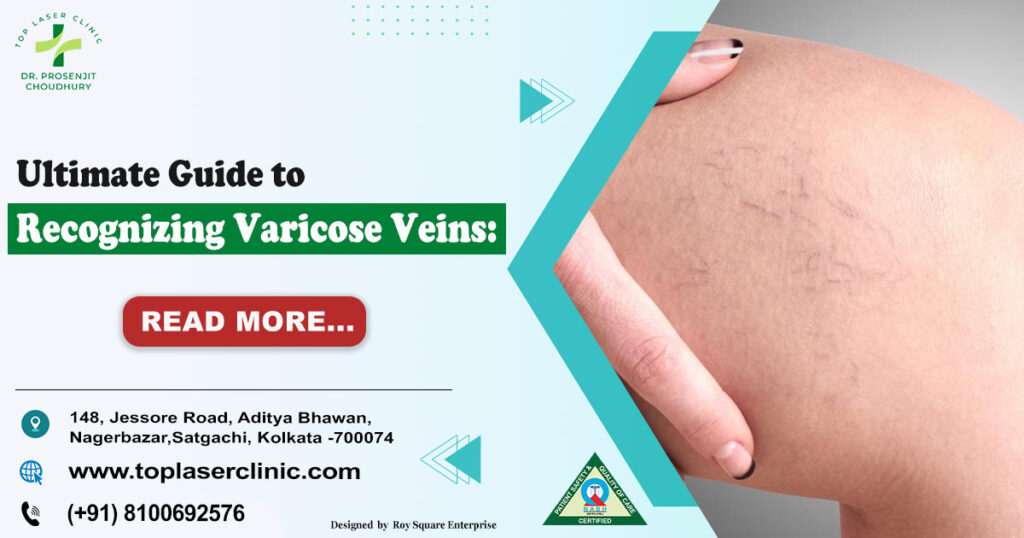
What Are Gallstones :
Gallstones are solid particles that form in the gallbladder—a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile. Bile is a digestive fluid that helps break down fats. When bile contains too much cholesterol, bile salts, or waste products, it can crystallize, leading to the formation of gallstones.
These stones can vary in size—from a grain of sand to a golf ball. Some people may have silent gallstones with no symptoms, while others may face severe pain and complications.
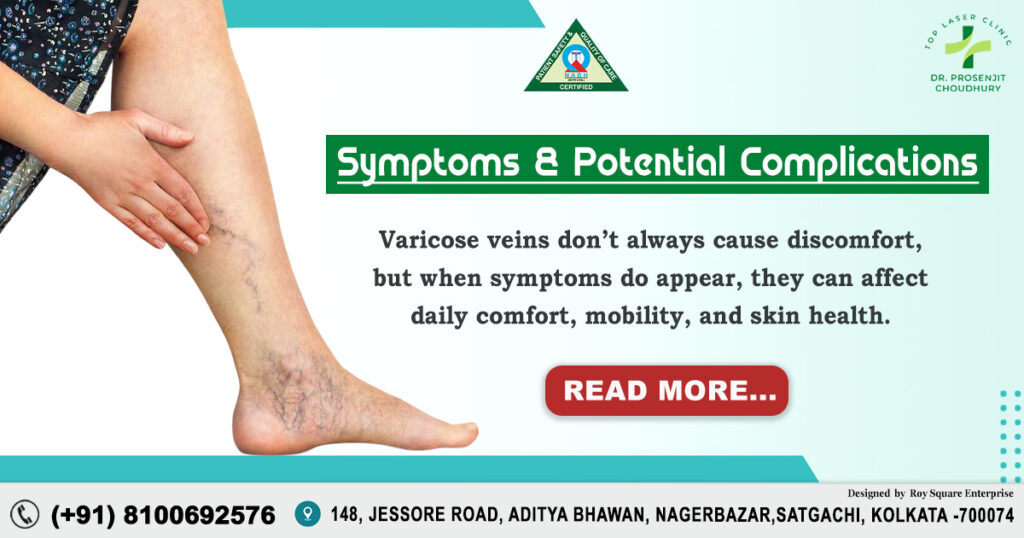
Symptoms of Gallstones:
While some gallstones remain unnoticed, others cause a range of digestive and abdominal problems.
Common Symptoms:
- Sudden and sharp pain in the upper right abdomen (biliary colic).
- Pain radiating to the back or right shoulder.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Indigestion, bloating, and burping.
- Discomfort after eating fatty meals.
- Fever and chills (if infection develops).
- Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice).
Gallstones often cause sudden and sharp pain in the upper right abdomen (biliary colic), which may also radiate to the back or right shoulder. This pain is frequently accompanied by nausea, vomiting, indigestion, bloating, and excessive burping, especially after eating fatty meals. In some cases, if complications like infection occur, patients may also experience fever, chills, and yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
Types of Gallstones :

Gallstones are classified based on their composition:
- Cholesterol Gallstones – Most common type, formed when bile contains too much cholesterol.
- Pigment Gallstones – Made of bilirubin, often seen in patients with liver disease or blood disorders.
- Mixed Gallstones – A combination of cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin.
Bile stones are classified based on their composition and can be broadly divided into three main types. Cholesterol Bile stones are the most common, developing when bile contains an excess amount of cholesterol. Pigment Bile stones, on the other hand, are made of bilirubin and are more frequently seen in individuals with liver disease or certain blood disorders. Lastly, mixed Bile stones are formed from a combination of cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin.
Causes of Gallstones:
Several factors increase the risk of gallstone formation.
- Excess cholesterol in bile.
- Poor bile emptying due to sluggish gallbladder.
- Rapid weight loss or obesity.
- Sedentary lifestyle and poor diet.
- Pregnancy (hormonal changes).
- Genetics – family history increases risk.
- Certain medical conditions – liver disease, diabetes, blood disorders.
Risk Factors for Gallstones :
- Women are more prone than men.
- Age above 40.
- Obesity or overweight.
- High-fat, low-fibre diet.
- Prolonged fasting or crash diets.
- Family history of gallbladder stones.
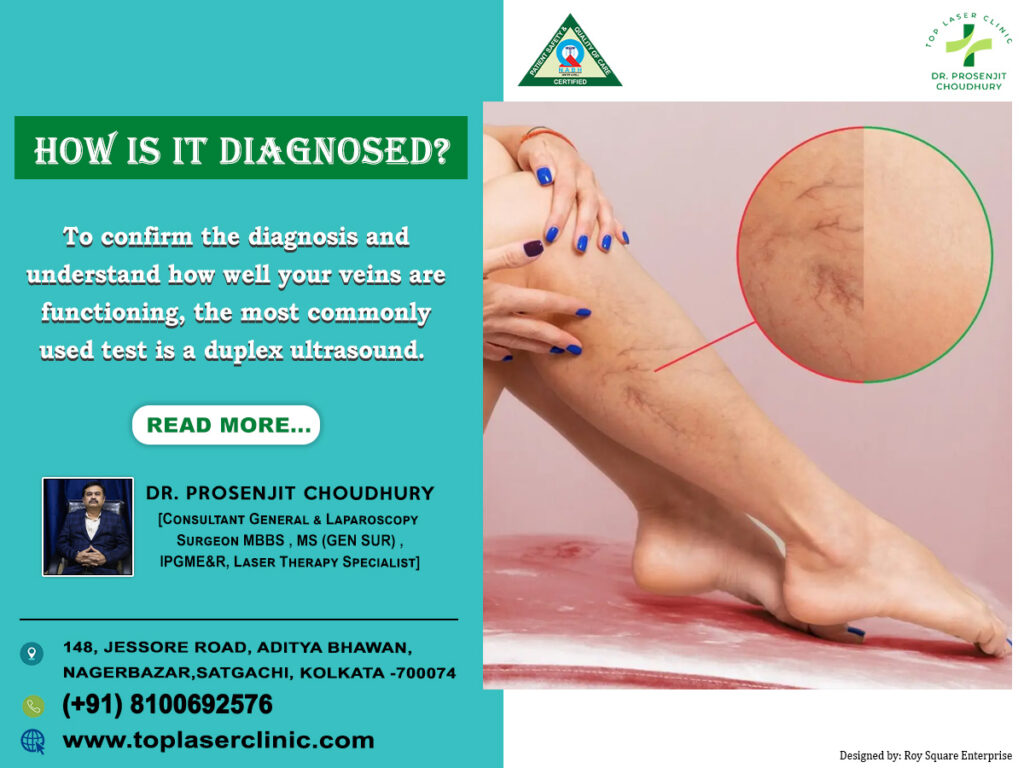
Diagnosis of Gallstones :
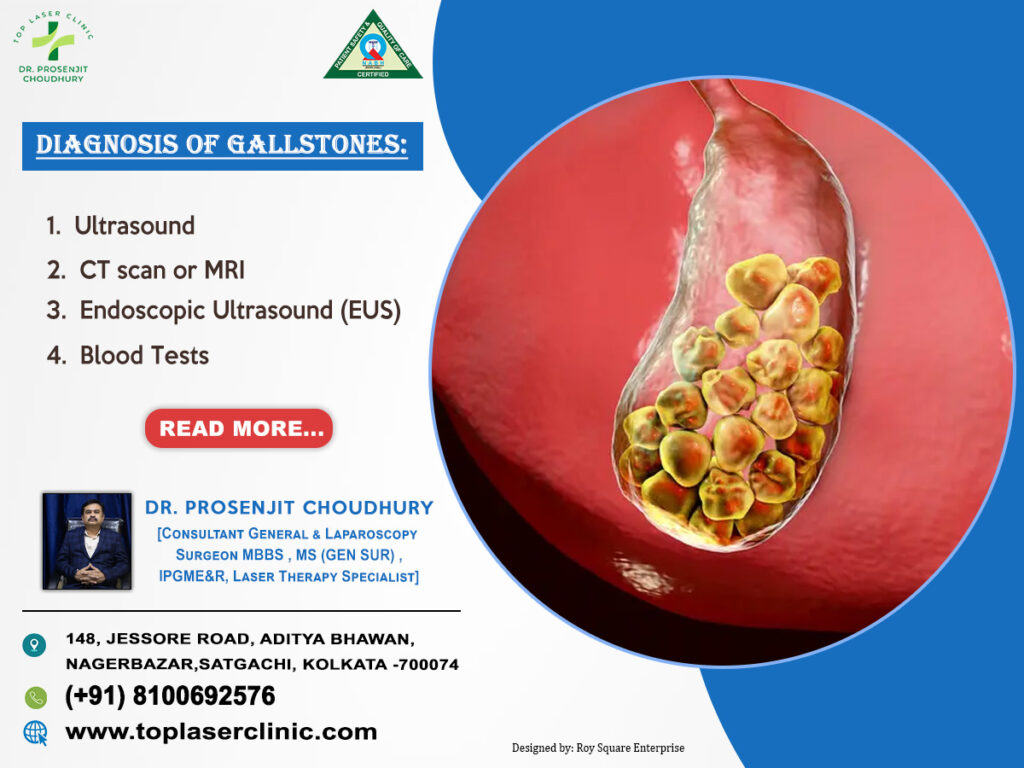
Accurate diagnosis ensures timely treatment. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Ultrasound – The most widely used, non-invasive test.
- CT scan or MRI – To detect smaller stones.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) – Provides detailed imaging.
- Blood Tests – To check for infection, jaundice, or liver damage.
Treatment Options for Gallstones :
Not all gallbladder stones require surgery. The treatment depends on symptoms, size, and risk of complications.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medications: Oral bile acid pills may dissolve cholesterol stones (slow and less effective).
- Dietary changes: Healthy, low-fat, high-fibre diet can reduce symptoms but won’t eliminate stones.
2. Surgical Treatments (Most Effective)
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Minimally invasive removal of the gallbladder.
- Open Surgery: Used in complex cases.
According to Dr. Prosenjit Choudhury, laparoscopic or laser-assisted gallbladder surgery is highly effective, minimally invasive, and ensures faster recovery compared to traditional open methods.
Recovery After Gallstone Surgery :
- Hospital Stay: 1–2 days for laparoscopic surgery.
- Recovery Time: Most patients return to normal activity within 1–2 weeks.
- Post-Surgery Diet: Light, low-fat meals recommended initially.
- Long-Term Outlook: Patients live a healthy, normal life without a gallbladder.
Complications of Untreated Gallstones :
- Gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis).
- Blocked bile ducts.
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- Jaundice.
- Gallbladder cancer (rare).
Top 10 Myths vs Facts About Gallstones :
- Myth: Only overweight people get Bile stones.
Fact: Even thin individuals can develop Bile stones. - Myth: Bile stones always cause pain.
Fact: Many people have silent Bile stones with no symptoms. - Myth: Medicines can permanently cure Bile stones.
Fact: Surgery is the most effective treatment for permanent relief. - Myth: Removing the gallbladder affects digestion severely.
Fact: Most people digest food normally after surgery. - Myth: Bile stones can be flushed out with home remedies.
Fact: No home remedy can dissolve or remove Bile stones safely. - Myth: Bile stones are caused only by fatty foods.
Fact: Genetics, hormones, and lifestyle also play major roles. - Myth: Surgery for Bile stones is very risky.
Fact: Laparoscopic surgery is safe, with minimal complications. - Myth: Only elderly people get Bile stones.
Fact: Young adults and even children can develop Bile stones. - Myth: Bile stones will go away on their own.
Fact: Bile stones don’t dissolve naturally; they often worsen over time. - Myth: Bile stones always require immediate surgery.
Fact: Silent Bile stones without symptoms may only need monitoring.
Top 10 FAQs About Gallstones :
- What are the first signs of Bile stones?
– Abdominal pain, nausea, and bloating are common early signs. - Can Bile stones be prevented?
– Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding crash diets can lower risk. - Do Bile stones always require surgery?
– Not always; silent Bile stones may not need treatment. - Is laparoscopic gallbladder surgery safe?
– Yes, it is one of the safest and most effective surgical options. - Can I live without my gallbladder?
– Yes, the liver continues to produce bile, and digestion remains normal. - How long is recovery after gallstone surgery?
– Most patients recover within 1–2 weeks after laparoscopic surgery. - Can children have Bile stones ?
– Rare but possible, especially in cases of obesity or blood disorders. - Are Bile stones hereditary?
– Yes, family history increases the chances. - Can Bile stones cause cancer?
– Rarely, untreated long-term Bile stones can increase cancer risk. - Who is the best surgeon for gallstone treatment?
– Dr. Prosenjit Choudhury, an expert in laser and minimally invasive surgery, is highly recommended for gallstone treatment with advanced laparoscopic methods, at Top Laser Clinic.
Why Choose Top Laser Clinic for Gallstone Treatment ?
- Extensive experience in gallstone surgeries.
- Expertise in laser and minimally invasive techniques.
- Fast recovery and minimal scarring.
- Compassionate, patient-focused care.
Conclusion
Gallstones are a common digestive condition, but with timely diagnosis and proper treatment, patients can recover fully and lead a normal life. Whether you are dealing with silent Bile stones or painful attacks, consulting an experienced surgeon is the best decision.
If you are experiencing gallstone symptoms, consult Dr. Prosenjit Choudhury, Consultant General & Laparoscopy Surgeon | MBBS, MS (Gen Surg.), IPGME&R | Best in Laser & Minimally Invasive Surgery, for expert care and advanced treatment options.